Intorduction
The recent statistical report says that, in the continent of Africa there are more than 200 languages spoken by the people.To be specific the number of languages, spoken in African continent lies between 2000 and 3000 languages.
Apart from this there are over 8000 dialects, that fits into these 300 languages.The major four classification of language families that are spoken in Africa can be divided into six types namely
1)Afro - Asiatic
2)Nilo - Saharan
3)Niger - Congo A
4)Niger - Congo B
5)Khoi - San
6)Austronesian
The image below shows exactly where these kind of languages are spoken
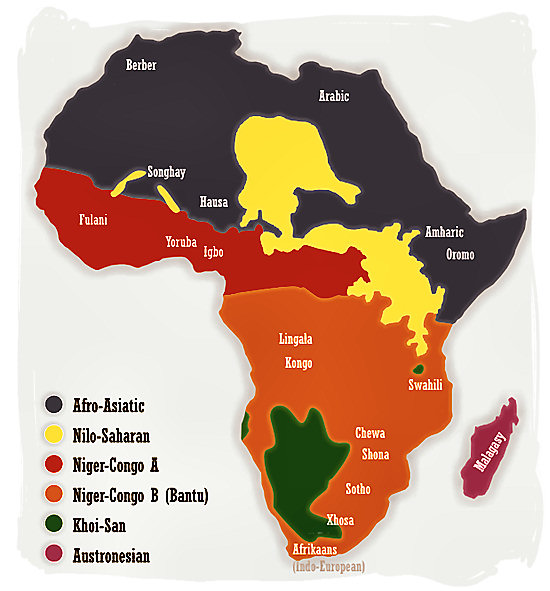
To be specific most these African Languages are group of languages that are native to the African continent(with some exception) and the the scholars estimate that out of these 3000 different kinds of languages 50 languages may have 500,000 or more speakers.
But the fact is that the majority of African languages are spoken only by relatively few people. For example languages like Hadza,which is spoken in Tanzania, unfortunately ranks among the languages with the fewest speakers, because reports says that only about 200 people speak this language and the people who speak this Hazda language are called as the Hazda people and the image belows shows the Hazda people

On the contrary the most widely spoken languages includes Swahili and Hausa and it is estimated that more than 50 million people speak Swahili, and this language is spoken by the people who live in East and Central Africa.
In the case of Hausa language, report says that about 25 million people speak this language, and primarily they are located in the West African country of Nigeria. Apart form these two languages other other African languages with large numbers of speakers includes
1)Fulfulde in Senegal, Cameroon, and Chad
2)Yoruba in Nigeria and Benin
3)Igbo in Nigeria.
But apart from all these reports the truth is that not all languages spoken in Africa are native to the continent. The Northern Africa speak Arabic as their first language, and it was brought to Africa by immigrants from Arabia between the 7th and the 11th centuries.
In the case of Madagascar Malagasy is the language spoken by most of the people, and belongs to the Austronesian group of languages with origins in Indonesia. Apart from this, starting from the 15th century the European colonists brought English, French, and Portuguese to Africa.
Niger - Congo Family
This Niger-Congo family descends from a protolanguage which has its history 5000 years back.It has been estimated that f rom30 crores to 40 crores of people in Africa used to speak the languages in the Niger-Congo . This Niger - Congo family has seven main subgroups.The image below shows the map of Africa, which shows variou languages spoken in different parts of the continent.

The seven subgroups of the Niger-Congo family includes
1)Benue-Congo (including Bantu)
2)West Atlantic
3)Mande
4)Voltaic
5)Kwa
6)Adamawa East and
7)Kordofanian.
1)Benue-Congo (including Bantu)
Out of this seven, six of which cover West Africa and the Central African Republic. One of the language which comes under the Benue-Congo is the Bantu language and is a single offshoot. This Bantu is spoken in most of the southern half of Africa.
The Benue-Congo subgroup is the largest branch of the Niger-Congo family.Report states that over 100 million people speak the Bantu language.
This Batu language is the largest rapidly growing language in Africa , with its users are rapidly increasing.Historians and archaeologists found a reason for this and they have found that the rapid expansion of Bantu languages begin from the proto-Bantu in Cameroon and eastern Nigeria and history reveals that it occurred in three major waves of migration, from 3000 to 4000 years ago.
These researches says that the first wave of expansion was created in North Bantu and it was succedde by the second and third expansions which was developed into Western and Eastern Bantu.
Of these Bantu languages, the most widely spoken language is Swahili and in Africa there are some 50 million speakers,and they are mostly concentrated to Eastern Bantu.Apart from this Bantu language, other Bantu languages are given below based on the region where they are used by the people
Bantu Languages spoken in Southern Africa:
i)Shona
ii)Tswana
iii)Zulu
iv)Xhosa
Bantu Languages spoken Eastern Africa:
i)Kikuyu
ii)Kisukuma
iii)Luo
Bantu Languages spoken Central Africa:
i)Kikongo
ii)Kinyarwanda
iii)Kirundi
2)West Atlantic
The West Atlantic subgroup are spoken mostly near the Africa’s Atlantic coast,and the countries which speak these languages includes from Senegal to Chad.In this family the dominant language which is used by most of the people is Fulfulde.
This Fulfulde has more than 13 million speakers and they are mostly used by people in Senegal, Cameroon, and Chad. Apart from this languages, other languages in this subgroup is
i)"Wolof" used in Senegal and
ii)"Temne" in Guinea.
3)Mande
Usually the languages in this sub group are spoken in
i)Senegal
ii)Mali
iii)Guinea
iv)Liberia
v)Sierra Leone.
In this subgroup Bambara,which is spoken in Mali, is considered the principal language .Other Mande languages in this catoegary includes
i)"Mende" spoken in Sierra Leone
ii)"Kpelle" spoken in Liberia and Guinea.
4)Voltaic
The other name for this Voltaic sub group is Gur,this language has speakers in different countries in Africa and it includes
i)Mali
ii)Cote d’Ivoire
iii)Ghana
iv)Togo
v)Benin
vi)Nigeria and
vii)Burkina Faso.
5)Kwa
The two most important language which comes under this subgroup includes the Twi and Yoruba, and they are mainly in Ghana and Nigeria respectively. Apart rom these two language, the language which is spoken widely in this subgroup is Yoruba, which has speakers of more than 22 million.
Other than these languages other Kwa languages are spoken in countries like
i)Liberia
ii)Cote d’Ivoire
iii)Togo and
iv)Benin.
6)Adamawa East
Most the languages of the Adamawa East subgroup are spoken widely in three important countries and these includes
i)Cameroon
ii)The Democratic Republic of the Congo (formerly Zaire) and
iii)The Central African Republic.
7)Kordofanian
The last subgroup of the Niger- Congo family is the Kordofanian subgroup and it has fewer than 500,000 speakers and they are found especially in the Nuba mountains of Sudan. The important language under this sub divison is Moro and it has about 30,000 speakers
Afro -Asiatic Family
Features of Afro - Asiatic family
The languages belong to this Afro-Asiatic family is spoken by around 20 crores to 30 crores people in Africa.Usually the languages to Afro-Asiatic family shares many features and one shared feature is the emphatic consonant, i.e, the amount of stress which the speaker places on a consonant changes for the meaning of certain words.
For example,let us consider the language of one of the subgroup of this family Hausa. In Hausa word "mana" literally means “for us,” whereas with an emphatic pronunciation of the consonant n in manna, it means “press against.”
Apart from this the languages in this family, also distinguish between masculine and feminine nouns.In the case of the feminine nouns, they typically have a final t. For example, in one of the language in this family , i.e,. in the language called Amharic, the word for man is "sew" and for woman is "set" and similary "ligu" means boy, and "ligitu" means girl.
Distribution
The main region where lots of people spek the languages belong to this family includes, the speakers from
i)Northern Africa
ii)Somalia
iii)Ethiopia
iv)Eritrea and
v)The area around Lake Chad in central Africa.
Subgroups
Usually when we look into this Afro - Asiatic languages, the basic vocabulary which they use reflects a pastoral life spent raising and herding livestock and also growing food crops.Under this Afro-Asiatic family , there is further divison and it is divided into five subgroups and these five subgroups usually contains more than 350 languages
The 5 subgroups of the Afro - Asiatic family includes
1)Chadic
2)Berber
3)Semitic
4)Cushitic and
5)Egyptian.
History goes wayback in years with respect to this family of languages, as the protolanguage of this family, which began to diverge into separate branches about 6000 years ago,and so it is called as ancestral Semitic.This family is also the protolanguage of other Semitic languages, which includes Arabic and Hebrew.Now let us disscuss each of this subgroup in detail.The image below shows the distribution of these sub groups in Africa
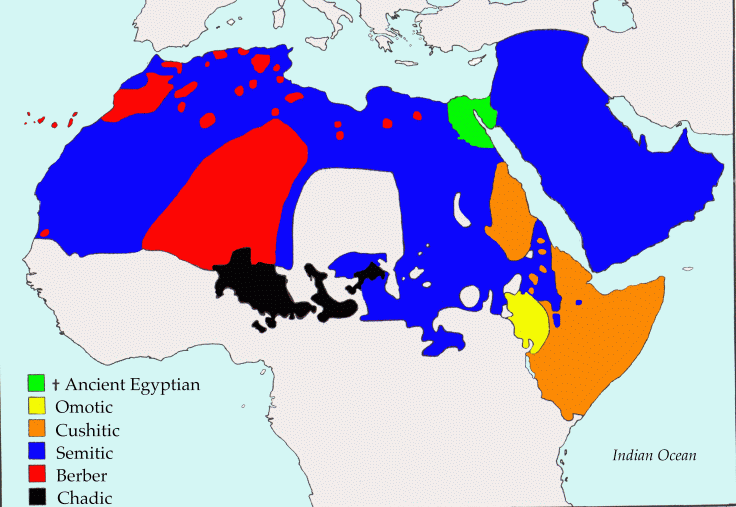
1)Chadic
#)This sub group consists of more that 100 languages
#)The number of speakers for this language is about 3 crores people
#)So naturally this language is considered as the most spoken language for this subgroup
#)This made this language as the most important language of this family.
#)Of this subgroup,the principal language is Hausa and it is also the most important language in the Afro-Asiatic family.
#)More than 2.2 crore of people speak Hausa and the consider this as their first language or some people consider this as fluent second language
#)The people speaking Hausa are conined mainly in the region of Northern Nigeria and southern Niger.
#)Apart from these large number of speakers for Hausa,it also serves as the lingua franca,i.e, this is language which is used for trade and communication especially in Western African countries like Senegal and Cote d’Ivoire, and also in some parts of Libya.
#)But historians believe that Hausa has borrowed many words from neighboring languages, such as Yoruba, Tuareg and also extensively from Arabic.
2)Berber
#)The number of speakers for this language is about 1.1 crores people and it is confiend mostly to Northern Africa
#)The most dominant language of this group,is Tamarshak (also spelled as Tamasheq),and it is spoken by the Tuareg people.
3)Semitic
#)Semitic languages includes languages like Amharic and Tigrinya
#)Their linguists trace back to Ge’ez,which is a type of language spoken mostly in northern Ethiopia more than 2000 years ago.
4)Cushitic
#)The principal languages includes Beja and Oromo
#)Beja language is spoken in Sudan and Eritrea
#)The languauge Oromo is mostly spoken in Ethiopia.
5)Egyptian
#)The history for this Egyptian subgroup of language goes back to 5000 years ago
#)But unfortunately historians believ thaese Egyptian language has not been spoken for about 600 years.
#)The last and final phase of this groups is the language called as as Coptic, remains alive as the liturgical language of the Coptic Church.
Nilo - Saharan family
The Nilo-Saharan languages are mostly tonal and some of the Nilo-Saharan languages add both prefixes and suffixes to verbs while others add only suffixes.
However the Nilo-Saharan languages do not have a noun class agreement system like that of the Bantu languages of the Niger-Congo family.This Nilo-Saharan language family mainly covers the following regions
i)Most parts of Eastern Sahara
ii)The upper Nile Valley
iii)Areas around Lake Victoria in east central Africa and
iv)The Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Around 1.8 crores tp 3 crores of people speak the languages which comes under this Nilo - Saharan languauge family.This Nilo-Saharan language family is divided into six subgroups and these includes
1)Nilotic (or Chari-Nile)
2)Songhai
3)Saharan
4)Maban
5)Koman and
6)Fur.
The ancestral language tongue was spoken was more than 1000 years ago and it is mainly spoken by the people in the Sahara between Chad and the Nile.
1)Nilotic (or Chari-Nile)
Out of the above six subgroups, Nilotic language is spoken widely,and this language is spoken along the Nile and Chari rivers. Languages in this subgroup includes
i)Luo - spoken in Kenya
ii)Masai (or Maasai) - spoken in Kenya and Tanzania and
iii)Nubian - spoken along the Nile Valley in Sudan and Egypt
Apart from the above languages, other languages in this subgroup are spoken mainly in countries mentioned below
i)Chad
ii)Ethiopia
iii)Uganda
iv)The Democratic Republic of the Congo and
v)The Central African Republic.
2)Songhai
Next subgroup is the Songhai and it is spoken along the Niger River in Mali and Niger.
3)Saharan
The Saharan subgroup group comprises languages that includes
i)Kanuri - spoken in Nigeria
ii)Teda - spoken in central Sahara and
iii)Zaghawa - spoken in Chad and Sudan.
4)Maban
Maban subgroup is spoken in mainly in Chad
5)Koman
The languages which are spoken under the Koman subgroup and they are mainly spoken along the portion of the border between Ethiopia and Sudan.
6)Fur
The last subgroup is the Fur subgroup and it is another small subgroup which is spoken in the Darfur province of Sudan.
Khoi - San language family
In the Khoi - San language family, more than 12 languages are available and it is divided into two subgroups
i)South African Khoi - San
ii)East African Khoi - San
Report says that there are around two lakhs to three lakhs people in Africa speak these languages.
Languages of South African Khoi - San:
The languages of South African Khoi - San includes
i)Nama
ii)Naron
These two type oflanguages are spoken mainly
i)In and around the Kalahari Desert of northern South Africa
ii)Southwestern Botswana
iii)Namibia
Languages of East African Khoi - San:
The languages of East African Khoisan mainly includes
i)Sandawe
ii)Hadza
These two type of languages are spokenmainly in Tanzania.
#)Many people were exposed to a Khoi - San language through the actor Nǃxau during the 1980 film The Gods Must Be Crazy.The image below shows some of the people who speak Kho - Sian language
