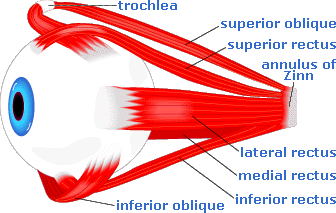
EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLES:
The extraocular muscles include voluntary muscles and involuntary muscles . The voluntary muscles are as follows
- Superior rectus
- Inferior rectus
- Medial rectus
- Lateral rectus
- Superior oblique
- Inferior oblique and
Levator palpabrae superioris


ORIGIN:
The 4 recti arise from common annular tendon or tendinous ring. The ring is attached to the apex of orbit. Lateral rectus has an additional origin from greater wing of sphenoid bone lateral to tendinous ring. Superior oblique arise from body of sphenoid and inferior oblique from maxilla. Levator palpabrae superioris arise from lesser wing of sphenoid.
INSERTION:
The recti and inferior oblique are inserted into sclera . Superior oblique is inserted into trochlear fossa of frontal bone and then attached to sclera.
Levator palpabrae superioris is attached to the superior tarsus. Levator palpabrae superioris has two parts namely membraneous part and muscular part called muller's muscle.
NERVE SUPPLY:
1) Superior oblique is supplied by trochlear nerve
2) Lateral rectus is supplied by abducent nerve
3) The muscular part of levator palpabrae superioris is supplied by cervical sympathetics
4) All the rest are supplied by oculomotor nerve
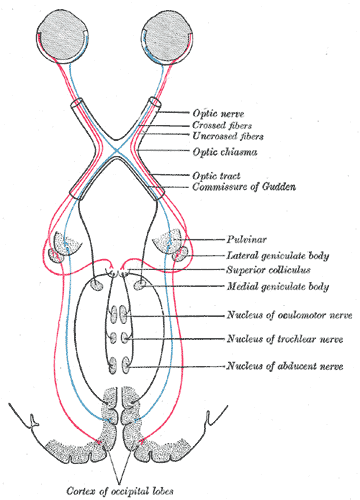
OCULOMOTOR NERVE:
It is a somatic motor nerve.Its functional components includes
- General somatic efferents for the movements of the eyeball
- General visceral efferents or parasympathetic for the contraction of the pupil and accomodation.
- General somatic afferent for proprioceptive impulses for the muscles of the eyeball.
Nucleus:
The oculomotor nucleus is located on the ventromedial part of the central grey horn of the midbrain at the level of superior colliculus.
The nucleus is connected to
- Pyramidal tract
- Pretectal nuclei
- 4th,6th,8th nerve nuclei
- Tectobulbar tract.
Course and distribution:
Arises from the nucleus and passes through tegmentum,red nucleus , substantia nigra and crus cerebri and runs in the interpeduncular cistern to reach the cavernous sinus.In the anterior part of the sinus it divides into anterior and posterior division.
The 2 divisions enter the orbit through the middle part of the superior orbital fissure.in the fissure nasociliary nerve lies in between the 2 division while abducent nerve lies inferolateral to them.
The upper division supplies the Superior rectus and Levator palpabrae superioris.The lower division supplies Medial rectus,Inferior rectus and Inferior oblique.the nerve to inferior oblique gives off motor root to ciliary ganglion.
Applied aspects:
A) Complete paralysis results in
- ptosis
- lateral squint
- dilatation of the pupil
- loss of accomodation
- proptosis and
- diplopia.

- A mid brain lesion causing contralateral hemiplegia and ipsilateral paralysis of the 3rd nerve is called weber's syndrome.
- Supranuclear lesions of the 3rd nerve causes loss of conjugate movements of the eye.
CILIARY GANGLION:
* It is the peripheral parasympathetic ganglion placed in the course of oculomotor nerve.
* It has 3 roots namely
- motor root
- sensory root and
- sympathetic root.
Motor root:
EDINGER WESTPHAL NIUCLEUS

OCULOMOTOR NERVE

ITS INFERIOR DIVISION

NERVE TO INFERIOR OBLIQUE

CILIARY GANGLION.RELAY OCCURS.

POSTGANGLIONIC FIBRE PASS THROUGH
SHORT CILIARY NERVE

SPHINCTER PUPILLAE AND CILIARIS MUSCLE.
Sensory root:
It comes from nasociliary nerve. it does not relay in the ganglion.
Sympathetic root:
It is formed by the plexus around the internal carotid artery.Postganglionic fibres arise from the superior cervical ganglion and supplies the dilator pupillae.
TROCHLEAR NERVE:
Its functional components includes
- general somatic efferents for the lateral movements of the eyeball
- general somatic afferent for proprioceptive impulses from the superior oblique muscle.It reaches the mesencephalic nucleus of the trigeminal nerve.
Nucleus:
It is situated in the ventromedial part of the central grey horn of the midbrain at the level of inferior colliculus.it is connected to
- pyramidal tract
- 4th,6th,8th nerve nuclei
- tectobulbar tract.
Course and distribution:
Starts from the nucleus and pass through superior medullary velum and it decussates there.It is the only nerve which arises from the dorsal aspect.It winds around the superior cerebellar peduncle and enters the cavernous sinus.
It runs in the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus between oculomotor and opthalmic nerve.Itn the anterior part it crosses oculomotor nerve.It enters the orbit through lateral part of the superior orbital fissure.
Applied aspects:
When it is injured diplopia results.

ABDUCENT NERVE:
Its functional components includes
- general somatic efferents for the lateral movements of the eyeball
- general somatic afferent for proprioceptive impulses from the lateral rectus.It reaches the mesencephalic nucleus of the trigeminal nerve.
Nucleus:
It is located in the upper part of the floor of the fourth ventricle.
It is connected to
- pyramidal tract
- 4th,6th,8th nerve nuclei
- tectobulbar tract.
Course and distribution:
It starts from the nucleus and pass through trapezoid body,medial lemniscus, basilar part of pons,cisterna pontis and enters the cavernous sinus. It enters the orbit through the medial part of the superior orbital fissure.it lies inferolateral to oculomotor nerve abd nasociliary nerve.
Applied aspects:
- Paralysis of the abducent nerve results in
- convergent squint and
- diplopia.

2) 6th nerve palsy is due to raised intracranial prsessure.
ACTIONS:

Superior rectus -
- elevation
- adduction
- intortion.
Inferior rectus -
- depression
- adduction
- extortion
Medial rectus -
- adduction.
Lateral rectus
- abduction.
Superior oblique
- depression
- abduction.
- intortion.
Inferior oblique
- elevation
- abduction
- extortion
APPLIED ASPECTS:
- Weakness causes squint or strabismus.
- Incoordination of the extraocular muscles causes nystagmus(involuntary movements of the eyeball).
INVOLUNTARY MUSCLES:
These includes
- Superior tarsal
- Inferior tarsal and
- orbitalis.
Superior tarsal:
It is inserted into upper margin of Superior tarsus. It elevates the eyeball.
Inferior tarsal:
It extends from the fascial sheath of the inferior rectus and inferior oblique to the lower margin of Inferior tarsus.

It depress the lower eyelid.
Orbitalis.:
It bridges the inferior orbital fissure.Its action is uncertain.