Mediastinum:
The space between the two lungs in the thoracic cavity where the heart is located. It is surrounded by
Anteriorly: Sternum
Posteriorly: Vertebral column
Superiorly: Thoracic cavity
Inferiorly: Diaphragm

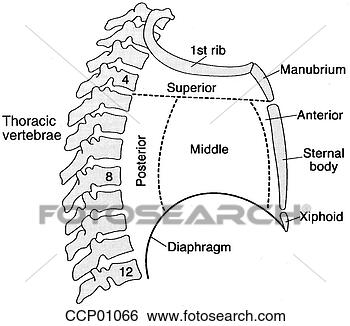
Sternum:
It is the flat bone located in the thoracic cavity.It has 3 parts namely
1)manubrium,
2)body and
3)xiphoid process.

Manubrium:
It has two surfaces namely anterior and posterior and has four borders:superior,inferior and 2 lateral borders.
attachments:
the anterior surface gives attachment to pectoralis major and sternocleidomastoid while posterior surface gives attachment to sternohyoid and sternothyroid.lower half of the posterior surface is related arch of aorta while the upper half is related is to branches of arch of aorta namely
1)brachiocephalic trunk
2)left common carotid and
3)left subclavian artery.
Body of sternum:
It has two surfaces namely anterior and posterior, two lateral borders and two ends namely upper and lower
Attachments:
Anterior surface gives attachment to pectoralis major while posterior surface gives attachment to sternocostalis.
Attachments of Xiphoid process:
Anterior surface gives attachment to rectus abdominus while posterior surface gives attachment to diaphragm.Linea alba is attached to its lower end.

Thoracic vertebra:
There are 12 thoracic vertebra out of which 2 to 8 is difficult. Each vertebra has body ,spinous process, transverse process, pedicle and 2 costal articular facets.

Thoracic inlet:
Upper end of the thorax which is continous with the neck is called thoracic inlet.
Boundaries:
Anteriorly upper border of manubrium sternum.
Posteriorly superior surface of body of first thoracic vertebra.
On each side first rib.
Structures passing:
Trachea , oesophagus, branches of arch of aorta, internal thoracic artery, inferior thyroiod vein, vagus nerve, sternothyroid and sternohyoid.

Diaphragm:
It is muscular. The major openings are
1. Aortic opening at the level of T12 through which aorta, azygous vein and thoracic duct pass.
2. Oesophageal opening at the level of T10 through which oesophagus, gastric nerve and oesophageal branches of left gastric artery pass.
3. Vena caval opening at the level of T8 through which inferior vena cava and branches of right phrenic nerve pass.

Mediastinum is divided into
1. Superior mediastinum and
2. Inferior mediastinum
By imaginary line drawn at the level of sternal angle of louis(T4-T5)
inferior mediastinum is further divided into
1) anterior,
2)middle and
3)posterior
by the pericardium.The part in front of pericardium is the anterior pericardium and the part behind is the posterior mediastinum. The contents of pericardium forms the middle mediastinum.
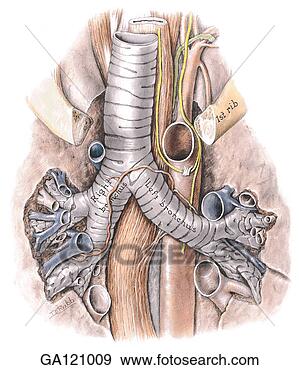
Boundaries of Superior mediastinum:
anteriorly manubrium
posteriorly T1-T4 vertebra
superiorly thoracic inlet and
inferiorly imagionary line.
Contents:
1)trachea and oesophagus
2)arch of aorta and its branches
3)Svc and vagus
4)thymus and thoracic duct.
Boundaries ofAnterior mediastinum:
anteriorly body of sternum
posteriorly pericardium
superiorly imagionary line
inferiorly diaphragm.
Contents:
1)lymph node and lymphatics,
2)thymus and
3)internal thoracic artery.

Boundaries of Middle mediastinum:
anteriorly sternum
posteriorly oesophagus,azygous vein and descending thoracic aorta
Contents:
1)heart
2)ascending aorta,pulmonary trunk dividing into right and left pulmonary artery,Svc,phrenic nerve.

Boundaries of Posterior mediastinum:
anteriorly pericardium
posteriorly lower 8 thoracic vertebra.
Contents:
1)oesophagus
2)descending thoracic aorta
3)azygous,hemiazygous,accessory hemiazygous vein
4)vagus and thoracic duct.

Applied anatomy:
1)any infection in the pretracheal and prevertebral fascia can spread into the superior mediastinum and posterior mediastinum.
2)since there is large space there is more chance of fluid collection.